Bio Gas-Future Fuel
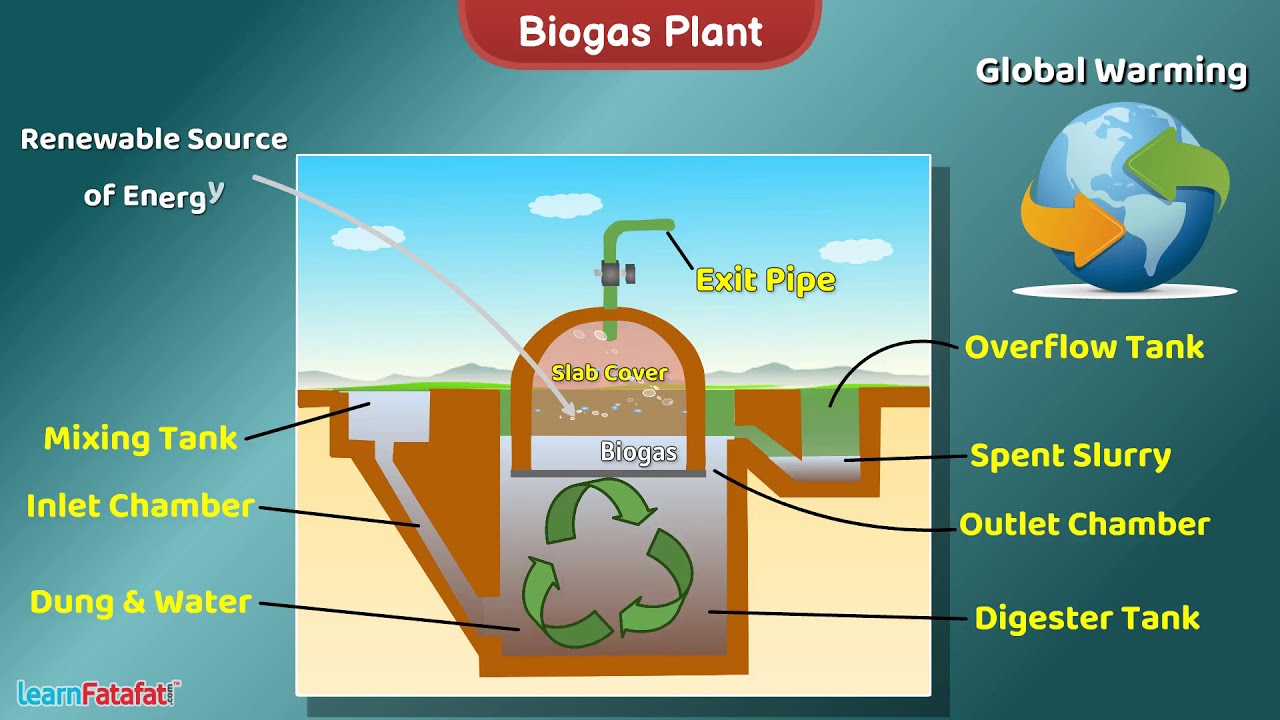
Biogas is a renewable energy source that’s produced by breaking down organic matter with bacteria in the absence of oxygen. This process is called anaerobic digestion.
Biogas is a mixture of methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide.
It can be produced from: Agricultural waste, Food waste, Animal dung, Manure, Sewage.
Biogas has many uses, including:
- Cooking gas
- Electricity production
- Water heating
- Space heating
- Replacing compressed natural gas in vehicles
- Displacin carbon dioxide in on-site CHP plants
Biogas is also known as gobar gas.
Is bio gas the same as gobar gas?
Yes, biogas is also known as gobar gas. The term “gobar” comes from Hindi and means “cow dung”. Gobar gas is biogas that’s produced from cow dung.

Gobar gas is a mixture of: Methane, Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen, Hydrogen sulfide.
The main component of gobar gas is methane.
What is the chemical composition of biogas?
The chemical formula for biogas is CH4, CO2, H2, and a trace amount of H2S.
The chemical composition of biogas is:
- Methane: 50–70%
- Carbon dioxide: 25–50%
- Nitrogen: Less than 5%
- Hydrogen: Less than 1%
- Oxygen: Traces
The chemical composition of biogas can vary depending on the type of plant biomass.
What is the difference between LPG gas and bio gas?
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a fossil fuel made from the refining of crude oil or natural gas. It’s a mixture of hydrocarbon gases, mainly butane and propane.
LPG can be 100% propane, 60% propane and 40% butane, or 35% propane and 65% butane. LPG is highly flammable and is used as fuel in household cooking and some automobiles.
Biogas is a renewable fuel made from the anaerobic digestion of organic waste.

It’s mainly methane from decomposing biomass.
Biogas is typically 50–75% methane, 25–50% carbon dioxide, and 2–8% nitrogen.
It also contains trace amounts of other gases, such as hydrogen, sulfur compounds, and nitrous oxide.

Biogas is more efficient and sustainable than LPG, with a lower environmental impact. Biogas production from organic waste can reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel systems.
What are 5 disadvantages of biogas?
some disadvantages of biogas:
- Impurities: Biogas contains impurities that are difficult to control.
- Corrosion: When compressed for fuel, biogas can corrode the metal parts of an engine.
- Foul odor: Biogas plants emit a foul odor from the wastes they process.
- Scum formation: Scum is a layer of dirt or froth that traps biogas inside the digester.
- Health and safety risks: Biogas plants can pose health and safety risks, including:
- Fire and explosion
- Confined space hazards
- Risk of asphyxiation
- Risk of gas poisoning
- Risk of high-pressure gas or liquid leaks
- Risks associated with rotating mechanical equipment
- Risks associated with pathogens
-
Other disadvantages of biogas include:
- Not efficient enough on a large scale
- Not economically viable
- Temperature-sensitive procedure
- Unstable and hazardous
Read About: India announced blending CBG in CNG and PNG