Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023 report released by Climate Policy Initiative
Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023 report released by Climate Policy Initiative
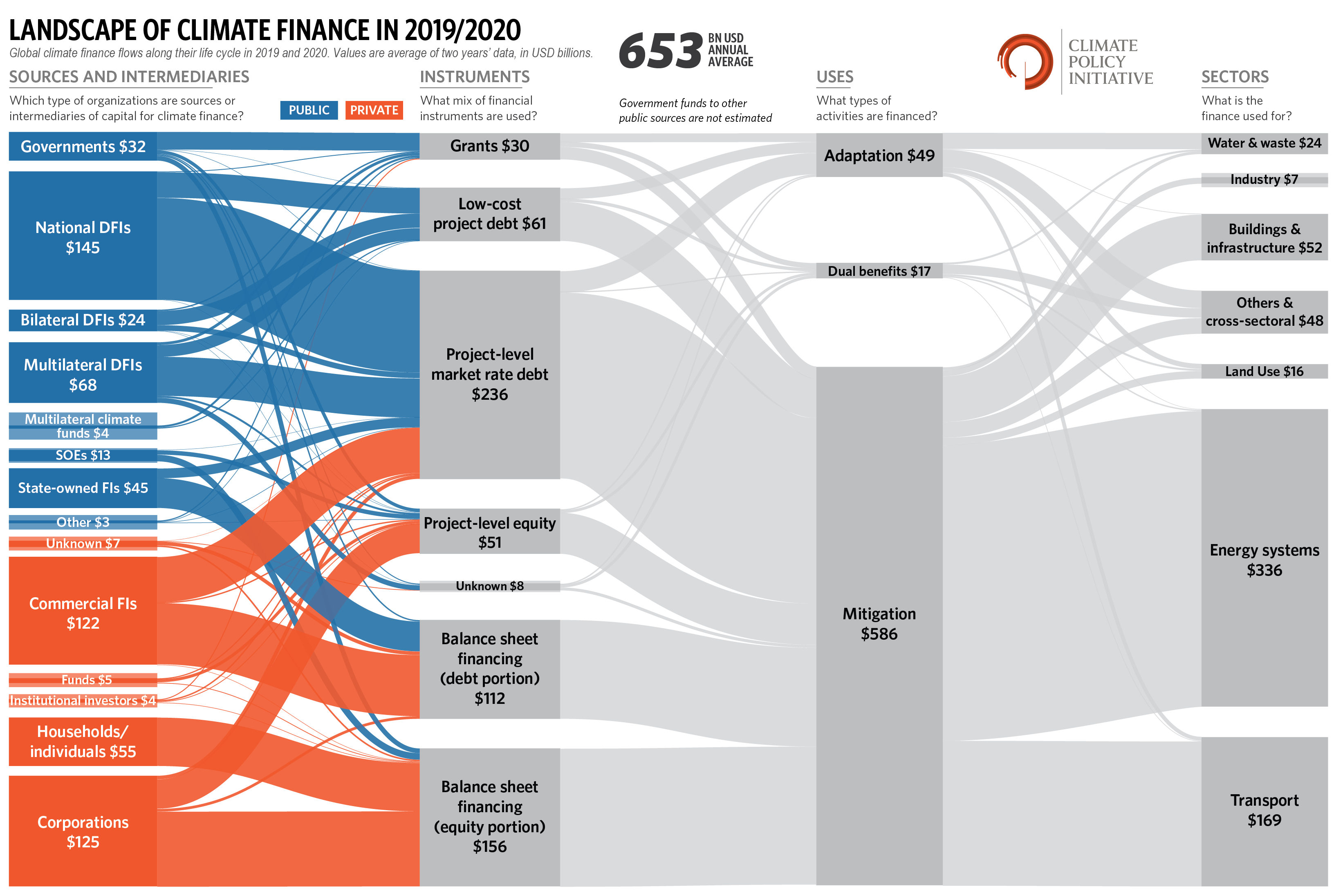
Private actors provided 49% of total climate finance (USD 625 billion). As with mobilizing domestic sources of finance, developed economies are much more successful at mobilizing private finance than EMDEs. The largest private sector growth came from household spending, which reached 31% of all private finance.
Climate finance refers to financing, from public, private, and alternative sources, that seeks to support mitigation and adaptation actions to address climate change.
- Mitigation tackles the causes of climate change, whereas adaptation tackles the effects of climate change.

Key highlights of the report
- Average annual climate finance flows reached almost USD 1.3 trillion in 2021/2022, nearly doubling than the
previous year. - China, the US, Europe, Brazil, Japan, and India received 90% of increased climate finance.
- Climate finance is uneven across sectors, energy and transport continue to attract the majority of flows: Private actors provided 49% of total climate finance.
- Adaptation finance continues to lag, with 98% coming from the public sector.
Recommendations
- Reforming international financial institutions, with rules, and incentives aligned with climate needs.
- Leveraging concessional finance to expand private flows.
- Mainstreaming climate adaptation and resilience into financial systems
- Phasing out unabated fossil fuels through a just transition
- Making climate finance data widely available and accessible.
- Work across countries to harmonize and enhance interoperability.
Global Climate finance mechanisms
- Global Environment Facility (established in 1992 Rio Earth Summit): It is a unique partnership of 18 agencies working with 183 countries to address the world’s most challenging environmental issues.
- Adaptation Fund, established in 2001 to finance concrete adaptation projects and programmes in developing countries Parties to the Kyoto Protocol.
- Special Climate Change Fund (SCCF), was established in 2001 to finance projects relating to: adaptation; technology transfer and capacity building; energy, transport, etc.
- Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF), was established to support a work programme to assist Least Developed Country Parties in carrying out the preparation and implementation of national adaptation programmes of action (NAPAs).
- Green Climate Fund (established under the Cancún Agreements in 2010), is mandated to support developing countries in raising and realising their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) ambitions
