Government launches Star Labeling Programme (SLP) for Solar Photovoltaic Modules (PVM)
The programme will help citizens to make an informed decision while deploying solar PVM or solar panels.
- Solar panels convert light energy captured from Sun into electric energy.
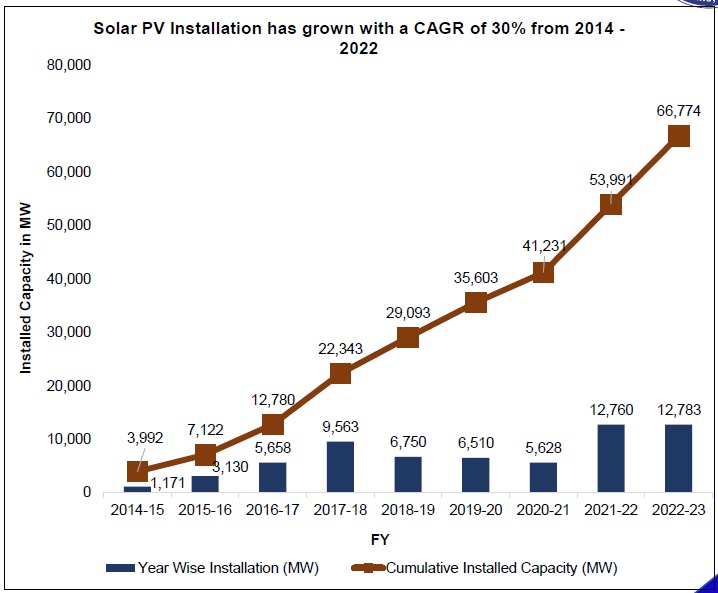
- In India, solar panel installation has grown with a CAGR of 30% from 2014 to 2022.
this also contributes to the government’s larger goal of enhancing the share of renewable energy and reducing emission intensity of GDP by 45% by 2030.
Growth of Solar Panels has been exponential, another 200 GW of solar panels to be added between now and 2030
❑ India has embarked upon an ambitious program, to achieve 40% of electric power installed capacity from renewable energy sources by 2030.
❑ Solar PV modules can be categorized based on the capacity of the modules and on the types of cell technology. Solar PV modules range from 5W to 500 W.
❑ Objective of S&L program for Solar PV is to help the Indian customers to make an informed decision and contribute towards GoI’s larger goal of enhancing the use of RE, in more efficient manner.
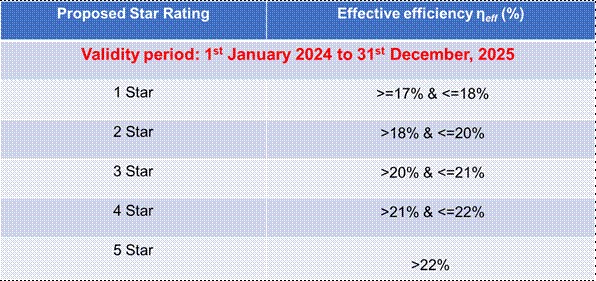
it is expected that the Solar PV module efficiency will enhance by 2% over its existing levels. Owing to performance improvement, the electricity generation is expected to increase by 33GWh/year and this will offset ~27,000 tons of CO2 emission per annum.
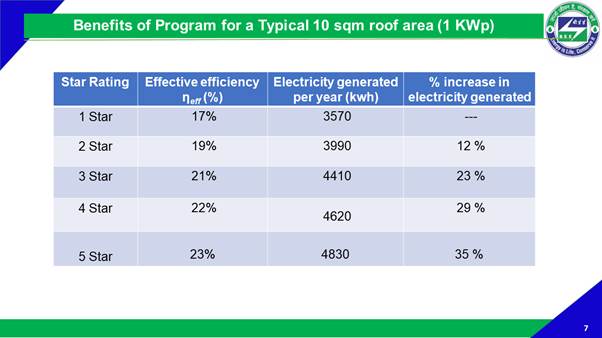
on a typical 10 square-metre roof area, a progression from 1-Star to 2-Star solar panel will result in additional electricity generation of around 12%, while the increase as compared to 1-Star solar panel can be as high as 29% – 35% for 4-Star and 5-Star panels.
As of now, 15 appliances are in mandatory regime, i.e., the appliances cannot be sold in the market without the label; and 19 appliances are in voluntary regime, where the market is in development stage.
List of 35 Appliances/Equipment
Mandatory
1. Frost Free Refrigerator
2. Direct Cool Refrigerator
3. Deep Freezers
4. Room Air Conditioner (Variable Speed)
5. Room Air Conditioner (Fixed Speed)
6. RAC (Cassette, Floor Standing Tower, Ceiling, Corner AC)
7. Light Commercial AC Fixed Speed
8. Stationary Storage Type Electric Water Heater
9. Tubular Fluorescent Lamps
10. LED LAMPS
11. Ultra-High Definition (UHD) Televisions
12. Colour Television
13. Distribution Transformer
14. Ceiling Fan
15. Chillers
Voluntary
1. General Purpose Industrial Motor
2. Agricultural Pump Set
3. Domestic Gas Stove
4. Washing Machine (Semi/Top Load/ Front Load)
5. Computer
6. Ballast
7. Office Automation Products
8. Diesel Engine Driven Monoset
Pumps for Agricultural Purposes
9. Solid State Inverter
10. Diesel Generator Set
11. Microwave Oven
12. Solar Water Heater
13. Air Compressors
14. High Energy Li-Battery
15. Tyres/Tires
16. Side by Side/Multi Door Refrigerator
17. Pedestal Fan
18. Table/Wall Fan
19. Induction Hob
20. Solar PVM
It is voluntary for two years and will be compulsory after that.
Expected outcome
A progression from 1-Star to 5-Star solar PVM will result in additional electricity generation of around 35%.
Reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 30 million tonnes per annum by 2030.
About Star Labeling Programme (SLP)
Background: Launched in 2006 under Ministry of Power.
Objective: Provide consumers with an informed choice regarding the energy savings and thereby the cost-saving
potential of various energy-consuming appliances.
Implementation: By Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) which is established under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
♦ Star Rating of Commercial Buildings, Eco Niwas Samhita, Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT), etc. are also key initiatives of BEE.
Applicability: Mandatory for 15 appliances and voluntary for 20 (including Solar PVM).
Achievement: Emissions reduction of almost 58 million tonnes of CO2 per annum.
